
Tonsillitis – causes, side effects and treatments at NaturalPedia.com
Thursday, July 05, 2018 by Zoey Sky
http://www.naturalpedia.com/tonsillitis-causes-side-effects-and-treatments-at-naturalpedia-com.html
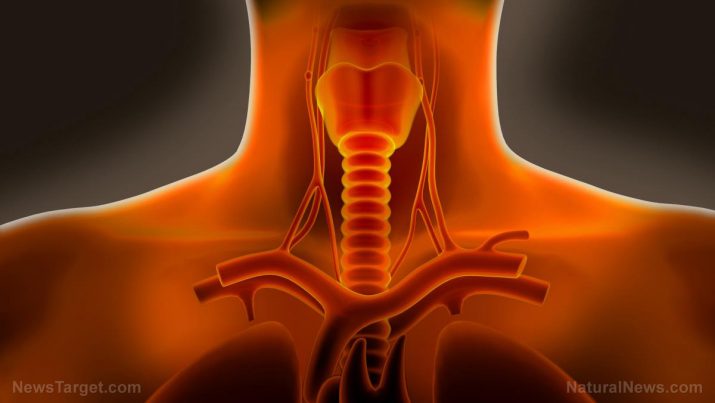
Tonsillitis occurs when the tonsils are inflamed (swollen) and infected.
Tonsils are the two lymph nodes located on each side of the back of the throat. A defense mechanism, tonsils protect the body from infection.
There are two types of tonsillitis:
- Recurrent tonsillitis – Involves several episodes of acute tonsillitis yearly.
- Chronic tonsillitis – Episodes last longer than acute tonsillitis. This type of tonsillitis comes with signs like bad breath/halitosis, chronic sore throat, and tender lymph nodes in the neck.
A person can develop the condition at any age, and tonsillitis is a common childhood infection. Children from preschool age through their mid-teens often develop tonsillitis.
Tonsillitis is contagious and it can be caused by different common viruses and bacteria, like Streptococcal bacteria (which causes strep throat). When left untreated, tonsillitis caused by strep throat may result in severe complications.
Tonsillitis is usually caused by viruses, like the Epstein-Barr virus, which can also cause mononucleosis.
Known symptoms of tonsillitis
The signs of tonsillitis usually include:
- Bad breath
- Chills
- Difficulty swallowing/painful swallowing
- Earaches
- Fever
- Headaches
- Jaw and neck tenderness (caused by swollen lymph nodes)
- Red and swollen tonsils
- A scratchy-sounding voice
- A stiff neck
- Stomachaches
- A very sore throat
- White or yellow spots on the tonsils
Very young children may experience excessive drooling and poor appetite. They may also be more irritable than usual.
Body systems harmed by tonsillitis
Tonsillitis may cause the following complications, especially if it is caused by bacteria:
- An infection of the middle ear
- Obstructive sleep apnea – Occurs when a patient’s throat walls relax while they are asleep. This may affect their breathing and sleep cycle.
- Quinsy – A collection of pus between a tonsil and the throat wall.
Rarer complications of the condition may include:
- Glomerulonephritis – This occurs when the filtering mechanisms of the kidneys swell and causes vomiting.
- Rheumatic fever – Causes inflammation all over the body. Rheumatic fever can also involve jerky body movements and joint pain.
- Scarlet fever
Food items or nutrients that may prevent tonsillitis
The following foods or nutrients can help prevent tonsillitis or address its signs:
- Echinacea
- Pineapple extract with bromelain
- Sage
- Selenium
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin E
- Wild indigo
- Zinc
Treatments, management plans for disease
Tonsillitis, especially mild cases, don’t require treatment, especially if it was caused by a virus, like a cold. However, treatment for more serious cases of tonsillitis includes surgery, intravenous fluids, or medication.
Surgery is advised for patients with tonsillitis that don’t respond to other treatment or those that cause complications. A tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure that removes the tonsils. Once a common procedure, it is now only recommended for patients with chronic/recurrent tonsillitis.
A dehydrated patient with tonsillitis may require intravenous fluids.
Medication can help relieve the sore throat of a patient with tonsillitis.
These home care tips can also help soothe a sore throat:
- Avoid smoke
- Gargle with warm salt water several times a day
- Get enough rest
- Stay hydrated
- Use a humidifier to moisten the air in your home
- Use throat lozenges
Where to learn more
- Help heal Tonsillitis and Chronic Sore Throat
- How Sage overcomes various conditions?
- Natural remedies for tonsillitis: 10 effective treatments you can pursue at home
- Understanding why you have allergies
- Use herbal and homeopathic treatments for tonsillitis
Summary
Tonsillitis occurs when the tonsils are inflamed (swollen) and infected.
The signs of tonsillitis usually include bad breath, chills, difficulty swallowing, and earaches.
Tonsillitis may cause complications like an infection of the middle ear, obstructive sleep apnea, or quinsy.
Tonsillitis, especially mild cases, don’t require treatment, especially if it was caused by a virus, like a cold. However, treatment for more serious cases of tonsillitis includes surgery, intravenous fluids, or medication.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: Tags: tonsillitis





