
Prostatitis – causes, side effects and treatments at NaturalPedia.com
Thursday, June 14, 2018 by Michelle Simmons
http://www.naturalpedia.com/prostatitis-causes-side-effects-and-treatments-at-naturalpedia-com.html
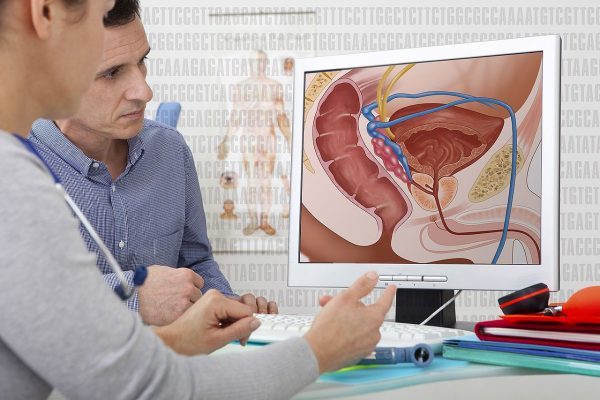
Prostatitis is a condition that involves inflammation of the prostate and sometimes the areas around the prostate, which frequently causes pain. There are four types of prostatitis: chronic prostatitis or chronic pelvic pain syndrome, acute bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatitis, and asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis.
The causes of prostatitis vary depending on the type. For chronic prostatitis or chronic pelvic pain syndrome, the exact cause is unknown. However, researchers believe that a microorganism, although not a bacterial infection, may cause the condition. This type of prostatitis may be related to the chemicals in the urine, the response of the immune system to a previous urinary tract infection (UTI), or nerve damage in the pelvic area. For acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis, these are caused by a bacterial infection. The acute type occurs suddenly and lasts only for a short period of time. On the other hand, the chronic type develops slowly and lasts for a long time, often years. The infection may occur when bacteria travel from the urethra into the prostate.
The risk factors for prostatitis also depend on the type. Men with nerve damage in the lower urinary tract caused by surgery or trauma may be more likely to develop chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. In addition, psychological stress may contribute to the development of the condition. Meanwhile, men with lower UTIs may be more likely to develop acute or chronic bacterial prostatitis. UTIs that recur or are hard to treat may result in chronic bacterial prostatitis.
Prostatitis is the most common urinary tract complication for men who are below 50 years old and the third most common urinary tract complication for men who are older than 50 years old.
Known side effects of prostatitis
The side effects of prostatitis also vary, depending on its type. The side effects of acute bacterial prostatitis include pain in the lower abdomen, lower back, or rectum, problem urinating, pain with urinating, chills, and a fever. A foul-smelling urine, pain the testicles, and painful ejaculation may also occur. The side effects of chronic bacterial prostatitis are similar to those of the acute type although they will be less severe.
Prostatitis can also result in other health complications, which may include bladder outlet obstruction or urinary retention, abscess typically in immunocompromised patients, infertility due to scarring of the urethra or ejaculatory ducts, recurrent cystitis, pyelonephritis, renal damage, and sepsis.
Body systems harmed by prostatitis
The body systems harmed by prostatitis are the urinary system as well as the reproductive system.
List of foods or nutrients that prevent prostatitis
There is no information on what foods or nutrients exactly prevent prostatitis. However, there are some foods that can help keep the prostate gland healthy. These include berries, such as strawberries, blackberries, and raspberries, which are rich in vitamin C and antioxidants; fatty fish, such as lake trout and herring, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids; nuts, such as Brazil nuts, pecans, almonds, and walnuts; beans, such as black beans, which will boost prostate health; green tea, which can help protect against prostate cancer; and watermelon, which is rich in vitamins A and C and lycopene.
Treatments, management plans for prostatitis
Treatments for prostatitis differ, depending on the type. Treatment options may include the following:
- Alpha-blocking agents
- Anti-inflammatory medicines together with sitz baths
- Avoiding caffeine, spicy foods, and alcohol, as these may trigger its symptoms
- Counseling
- Exercise
- Medicine for infectious prostatitis
- Myofascial trigger point release physical therapy
- Natural antioxidant bioflavonoid quercetin to improve inflammation and symptoms in nonbacterial prostatitis or chronic pelvic pain syndrome
- Progressive relaxation
Where to learn more
- What are the Signs and Symptoms of Prostatitis?
- Herbs for the male reproductive system
- Good Foods You Can Eat to Fight Candida
- A weed to some, plantain is a survivalist’s powerful medicine
- Healthy Diet For Prostate Problem In Men
Summary
Prostatitis is a condition that involves inflammation of the prostate and sometimes the areas around the prostate.
Prostatitis may cause pain in the lower abdomen, lower back, or rectum; problems urinating; pain with urinating; chills; and a fever.
Prostatitis may result in other health complications, such as bladder outlet obstruction or urinary retention; abscess typically in immunocompromised patients; infertility due to scarring of the urethra or ejaculatory ducts; recurrent cystitis; pyelonephritis; renal damage; and sepsis.
Prostatitis can be treated with alpha-blocking agents, medicines, avoiding caffeine, spicy foods, and alcohol, counseling, exercise, physical therapy, quercetin, and progressive relaxation.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: Tags: prostatitis





