
Dextrose – toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts
Tuesday, December 05, 2017 by Rita Winters
http://www.naturalpedia.com/dextrose-toxicity-side-effects-diseases-and-environmental-impacts.html
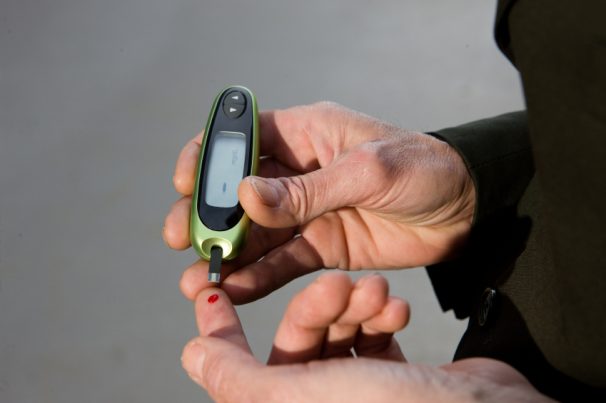
Dextrose, a monosaccharide otherwise known as D-Glucose, is a simple sugar made from corn. It is chemically identical to glucose or blood sugar and is often used in baking products and medical formulations. For medical purposes, dextrose is used to raise blood sugar levels quickly, and provides the body with extra water and carbohydrates (calories from sugar).
Other names and synonyms for dextrose include D-Glucose, D-Glucopyranose, Glucose, Glucopyranose, Grape sugar and D-Glc.
While dextrose is mainly used to help people with certain medical conditions, dextrose also has its share of negative side effects, especially with individuals with blood sugar disorders.
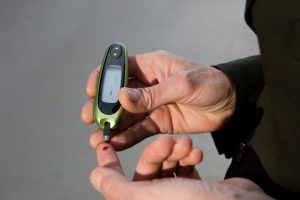
List of known side effects
Some symptoms of exposure to large quantities of dextrose include fruity odor in the breath, increasing thirst with no known causes, dry skin, dehydration, nausea, shortness of breath, stomach upset, unexplained fatigue or lethargy, frequent urination, vomiting, confusion, severe swelling of the extremities, fever and skin redness.
Dextrose can also cause some severe side effects. Hyperglycemia, or an abnormally high blood glucose level, can be a result of too much dextrose. Individuals with diabetes are prone to having hyperglycemia, due to the fact that their bodies do not produce enough or respond to insulin, leading to high levels of blood sugar. It can lead to tissue damage, coma and death.
Overdoses on dextrose may also lead to an inverse reaction. When blood sugar levels are high, the pancreas overreacts and overproduces large quantities of insulin. This then leads to hypoglycemia, or a lack in blood sugar. Feelings of nausea, hunger, and dizziness are some side effects of hypoglycemia.
This medical ingredient is also known to cause excessive fat storage, even without diabetes. Fat storage helps humans survive periods of starvation historically. Nowadays, people rarely rely on fat storage since food is easily accessible. Excessive fat storage leads to being overweight or obesity.
Body systems affected by dextrose
Dextrose overdose may damage the liver, pancreas, and other internal organs. It may also cause obesity which leads to negative side effects, including chronic diseases.
Items that contain dextrose
Some trade names of dextrose include Kabiven, Perikabiven, and SmartRx MLD Kit.
It is also used to make several intravenous preparations which are available only at hospitals or medical facilities. It is also available as oral gels or tables that can be bought over the counter at pharmacies, or as prescribed by doctors. Higher doses of dextrose are known to “rescue” individuals suffering from hypoglycemia.
How to avoid dextrose
Hospitals and other medical institutions make use of dextrose, especially during in-patient situations. It is best to avoid getting sick to avoid usage or overusage of dextrose.
Proper storage and disposal of this medicine must always be practiced. At home, dextrose products should be kept at room temperature or colder, away from heat and direct light. Used needles should be kept in hard containers that can be locked from children. There are pharmacies that offer medical waste disposal methods. Medicines, including delivery mediums like needles and syringes must be kept out of reach of children, and must not be handled by individuals who do not have training.
Where to learn more
- 6 Ways to DIY the Best Fruit Water Ever
- Sugar: What is Safe for Our Children?
- Yes, eating too much salt can harm your body… but the right kind of salt can boost your mineral intake
- Consumer watchdog group lowers safety rating of Splenda due to links with leukemia
- Conventional gum is gross; it’s time to switch to organic, courtesy of the rainforest
Summary
Dextrose is one of the most common ingredients in medical solutions.
Dextrose may not directly be fatal, but overdose may have severe side effects.
Dextrose is a form of sugar that may result in obesity and consequently, chronic diseases.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: Tags: dextrose





