
Candidiasis – causes, side effects and treatments at NaturalPedia.com
Friday, February 09, 2018 by Ralph Flores
http://www.naturalpedia.com/candidiasis-causes-side-effects-and-treatments-at-naturalpedia-com.html
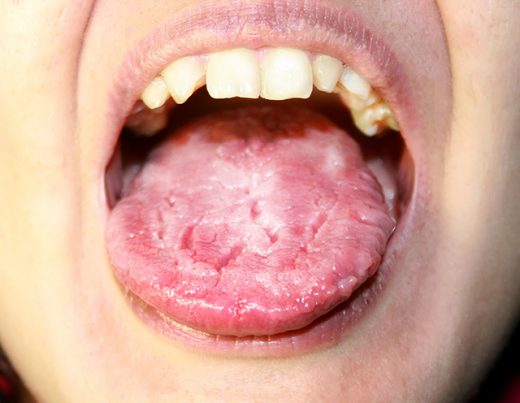
Candidiasis is the medical term for any fungal infection caused by the yeast from the Candida genus. Of the 20 pathogenic species of Candida yeast, the most common cause of the disease is Candia albicans; a fungus usually present in the skin and the mucous membranes such as the vagina, mouth, and rectum. However, a weakening of the immune system or antibiotic use causes an overgrowth of the yeast, making it into an infectious agent.
Yeast infections manifest in various forms, depending on the area of infection.
- Thrush is a yeast infection that is localized in the mouth and throat. It is also referred to as oropharyngeal candidiasis.
- Candida esophagitis, or esophageal candidiasis, is an infection located in the esophagus. This condition is common in people who have HIV/AIDS.
- Vaginal candidiasis happens when the environment inside the vagina changes (usually because of hormonal changes, illness, or antibiotic use), causing an overgrowth in the area.
- When the skin contracts candidiasis, it causes rashes and itching.
- Invasive candidiasis is a serious infection that affects the bloodstream. This is considered to be life-threatening, as it can potentially affect organs such as the heart, brain, eyes, bones, and other parts of the body.
There have also been cases of candidiasis from Candida auris, a drug-resistant strain of the Candida genus which has caused outbreaks in various healthcare facilities. Infections caused by C. auris are severe, as these can cause infection in the bloodstream, with one out of three cases invasive candidiasis caused by the fungus end up in death.
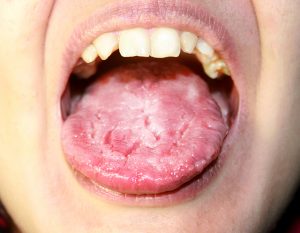
Known risk factors and symptoms of candidiasis
If a person is healthy, the C. albicans yeast is controlled by the immune system, making the likelihood of infection very low. However, any changes in the immune system — like illness or antibiotic — is a major risk factor for the development of the disease.
Moreover, any defects in the body, such as those listed below, may also increase the risk of infection:
- wounds and ulcerations in the skin
- a deficiency in phagocytic cells
- chronic granulomatous diseases which affect immune cells
- a disorder in monocytic cells responsible for antimicrobial activity
- complement disorders that affect antibody interaction
- immunoglobulin defects
- illnesses that affect cellular immunity such as HIV, diabetes mellitus, and medication that suppresses the immune system
- changes in protective bacteria flora caused by antibiotics
Aside from these, risk factors for more severe forms of the infection such as invasive or systemic candidiasis include:
- bone marrow transplantation
- solid organ transplantation
- chemotherapy and radiation therapy
- severe trauma
- recent surgery, particularly that of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract
- premature birth
- hemodialysis
The Candida species are normally found in a hospital setting; thus some procedures (such as intravenous and foley catheters, prolonged hospital stays, and mechanical ventilation) can also be a source of infection.
Depending on the area, symptoms of candidiasis appear differently. For oropharyngeal candidiasis, symptoms may include:
- white patches on the inner cheeks, tongue, the roof of the mouth, and throat
- redness or soreness
- a cottony feeling in the mouth
- loss of taste
- pain while eating or swallowing
- cracking and redness at the corners of the mouth
If a woman has vaginal candidiasis, some symptoms she may have include itching and soreness in the region, pain during sexual intercourse and urination, and abnormal vaginal discharge.
Body systems affected by candidiasis
Candidiasis primarily strikes the skin and the mouth; however, this may also affect other organs in the body, based on the locality of the infection.
Food items that may prevent and treat candidiasis
People who have candidiasis are not advised to consume sugars and other forms of refined carbohydrates, since this may aggravate the condition. Moreover, avoid dairy products, vegetables that contain starch, grains, alcoholic beverages, processed oils and meats, fermented food, and all forms of sugar (both artificial and natural).
Recommended food items to aid in treating candidiasis include eggs, fresh fish, lean meats, nuts and seeds, olive oil, and coconut milk. Unsweetened probiotic yogurt can also help prevent overgrowth.
Treating and managing candidiasis
For infections on the skin, most healthcare providers will recommend topical antifungal creams. When this is located inside the body, such as those with oropharyngeal candidiasis or Candida esophagitis, oral antifungal treatments will be used instead. Severe cases such as those from invasive candidiasis will depend on the level of white blood cells in the bloodstream, as well as other organs that have possibly been infected.
Surgery is an option only when there is a severe case of infection or abscess formation inside the body.
Where to learn more
- Woman overcomes systemic candidiasis with raw food diet
- Natural compounds to kill off yeast
- Seven herbs to fight yeast in the body
- 49 Health Benefits of Coconut Oil
- The Candida and Fungus Among Us
Summary
Candidiasis is an infection caused by yeast overgrowth in the body. This is usually a result of a change in the body’s immune system which causes the infection. The condition can be treated with medication, and there are food items available to treat and prevent it.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: Tags: Candidiasis





