
Anaplasmosis — causes, side effects and treatments at NaturalPedia.com
Wednesday, January 03, 2018 by Michelle Simmons
http://www.naturalpedia.com/anaplasmosis-causes-side-effects-and-treatments-at-naturalpedia-com.html
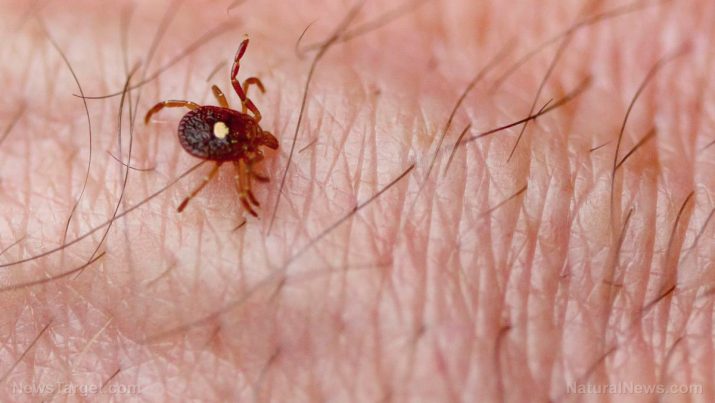
Anaplasmosis is a tick-borne disease caused by a microorganism known as Anaplasma phagocytophilum. It was previously known as human granulocytic ehrlichiosis (HGE), but it has lately been called human granulocytic anaplasmosis (HGA). It is also referred to as gallsickness or gall sickness. The initial symptoms of anaplasmosis usually begin within one to weeks after the bite of an infected tick. The tick bite is typically painless, and some patients who develop anaplasmosis do not remember being bitten.
The risk factors for HGA may include recreational activities, such as hiking, golfing, gardening, and camping, living in tick-infested areas, having a weak immune system, and staying outdoors during the spring and summer months, when the population of ticks are at their highest. This disease can also be transmitted in other ways aside from tick bites, through blood transfusions or when blood or blood products are contaminated, and from an infected pregnant woman to her unborn child. The disease can be diagnosed through physical examination, assessment of symptoms, blood test, polymerase chain reaction test, or indirect fluorescent antibody test.
Known side effects of anaplasmosis
According to an article published by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, a person who has been bitten by an infected tick may experience fever, headache, muscle pain, malaise, chills, nausea, abdominal pain, cough, confusion, or rash. Other side effects or symptoms of anaplasmosis may include difficulty in breathing, hemorrhage, renal failure, or neurological problems. It may also cause problems with the blood clotting process, bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, damage to liver, respiratory failure, and kidney failure.
This condition can be a severe illness if not treated correctly.
Body systems harmed by anaplasmosis
There are several body systems that can be harmed if a person gets infected with anaplasmosis. These include the muscular, nervous, integumentary, respiratory, digestive, and cardiovascular.
List of foods or nutrients that prevent anaplasmosis
There are no foods or nutrients that can particularly prevent anaplasmosis, but there are foods and nutrients that can be used as remedies for tick bites. These include oranges; foods rich in B vitamins such as brown rice, fish, and Brewer’s yeast; and onions.
Treatments, management plans for anaplasmosis
There are several treatments and management plans for anaplasmosis. People with anaplasmosis are generally treated with the use of tetracycline antibiotics. In addition, people with this disease may experience symptoms of headache, fever, and joint pain, which can be treated by certain natural medicines. Furthermore, bed rest may be needed as an important treatment measure for people with the disease.
Where to learn more
- Rare infectious bacteria thrive by hijacking human immune response
- Nutrients.news
- DangerousMedicine.com
- BigPharmaNews.com
- Herbs.news
Summary
Anaplasmosis is a tick-borne disease caused by a microorganism known as Anaplasma phagocytophilum.
Anaplasmosis can cause symptoms such as fever, headache, muscle pain, malaise, chills, nausea, abdominal pain, cough, confusion, or rash.
Anaplasmosis may cause difficulty in breathing, hemorrhage, renal failure, or neurological problems.
Anaplasmosis may cause problems with the blood clotting process, bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, damage to liver, respiratory failure, and kidney failure.
Foods and nutrients that can be used as remedies for tick bites include oranges; foods rich in B vitamins such as brown rice, fish, and Brewer’s yeast; and onions.
Anaplasmosis can be managed through non-strenuous activity, bed rest, and medicines.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: Tags: Anaplasmosis





