Human monocytic ehrlichiosis – causes, side effects and treatments at NaturalPedia.com
Wednesday, July 18, 2018 by Zoey Sky
http://www.naturalpedia.com/human-monocytic-ehrlichiosis-causes-side-effects-and-treatments-at-naturalpedia-com.html
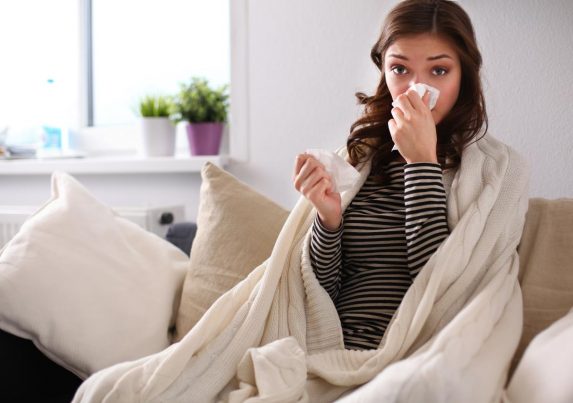

Human monocytic ehrlichiosis refers to a bacterial illness that is characterized by flu-like symptoms. When left untreated, the disease may cause severe complications. However, human monocytic ehrlichiosis can be cured with immediate medical treatment.
Human monocytic ehrlichiosis is caused by Ehrlichia chaffeensis (E. chaffeensis) bacteria.
The disease is usually spread via a bite from an infected lone star tick. Human monocytic ehrlichiosis can also be transmitted by deer ticks or dog ticks. Lone star ticks are can be found all over the southeastern and south central U.S. and in the East Coast. Female lone star ticks are identified through the white spot on their back.

Known side effects of human monocytic ehrlichiosis
Human monocytic ehrlichiosis is associated with different side effects, but the combination of these symptoms can vary depending on the patient.
The side effects of human monocytic ehrlichiosis usually include:
- Chills
- Confusion
- Diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting
- Fever
- A headache
- Malaise
- Muscle pain
- Rash (usually observed in 60 percent of children and in less than 30 percent of adult patients)
- Red eyes/conjunctival injection
Risk factors for human monocytic ehrlichiosis may include:
- Being older than 60
- Living in a tick-infested area
- Recreational activities (e.g., camping, gardening, golfing, and hiking, particularly in tick-infested areas)
- Working outdoors (e.g., forest workers)
- Being outside/outdoors during warm weather, like in the spring and summer months, which is when the population of the ticks is at their highest
Body systems harmed by human monocytic ehrlichiosis
If left untreated, human monocytic ehrlichiosis may cause the following complications:
- Ataxia/problems with voluntary muscle coordination
- Bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract
- Coma (usually occurs during severe cases of the disease)
- Dyspnea/shortness of breath
- Hyperreflexia/excessive response to sensory stimuli and other neurological problems
- Kidney and heart failure
- Meningitis
- Problems with blood clotting
- Respiratory failure
- Seizures
- Stiff neck and/or facial paralysis
Food items or nutrients that may prevent human monocytic ehrlichiosis
The following foods or nutrients can help prevent human monocytic ehrlichiosis or address its side effects:
- Ginger — Ginger can boost your immunity and it can help increase the white blood cells in the body, which will help fight the infection. Drink ginger tea regularly or take a spoonful of ginger juice mixed with warm water every morning.
- Licorice root — Licorice root can help regulate your immune system, which will help soothe the infection. Drink licorice tea with some lemon twice daily.
- Turmeric — Turmeric can help soothe itching and pain in the infected area. Drink some turmeric mixed with warm milk to address pain caused by the condition.
Treatments, management plans for human monocytic ehrlichiosis
Human monocytic ehrlichiosis is usually treated with medication such as antibiotics.
The following tips can also help prevent human monocytic ehrlichiosis:
- Check the back of your neck, ears, the back of the knees, groin area, and underarms for any ticks.
- Wear light-colored clothing so it’s easier to find any ticks.
- Wear long-sleeved shirts, full-length pants, and closed-toe shoes, especially when walking in grassy or wooded areas. Try to avoid these areas when possible.
- Tuck your shirt into your pants, then tuck your pants into your socks to help prevent tick bites.
- Remove ticks immediately to reduce the risk of infection.
Where to learn more
- Repel ticks with this natural oil
- Revolutionary diagnosis: A single blood test can now detect Lyme and other tick-borne diseases
- Tick bites can cause life-threatening allergic reactions to red meat
- Tick bite turns people into involuntary vegetarians
- Yarrow herb is stronger than DEET at repelling mosquitos and ticks, and it’s completely non-toxic
Summary
Human monocytic ehrlichiosis refers to a bacterial illness that is characterized by flu-like symptoms. It is caused by Ehrlichia chaffeensis (E. chaffeensis) bacteria.
The side effects of human monocytic ehrlichiosis usually include chills, confusion, and fever.
If left untreated, human monocytic ehrlichiosis may complications like ataxia, coma, dyspnea, or meningitis.
Ginger, licorice root, or turmeric can help prevent human monocytic ehrlichiosis or address its side effects.
Human monocytic ehrlichiosis is usually treated with medication such as antibiotics.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: Tags: Human monocytic ehrlichiosis